Blogs
Home
Blogs
PRP Treatment for Hair: Benefits, Procedure, Results & Cost Explained
December 23, 2024 • 4 min read
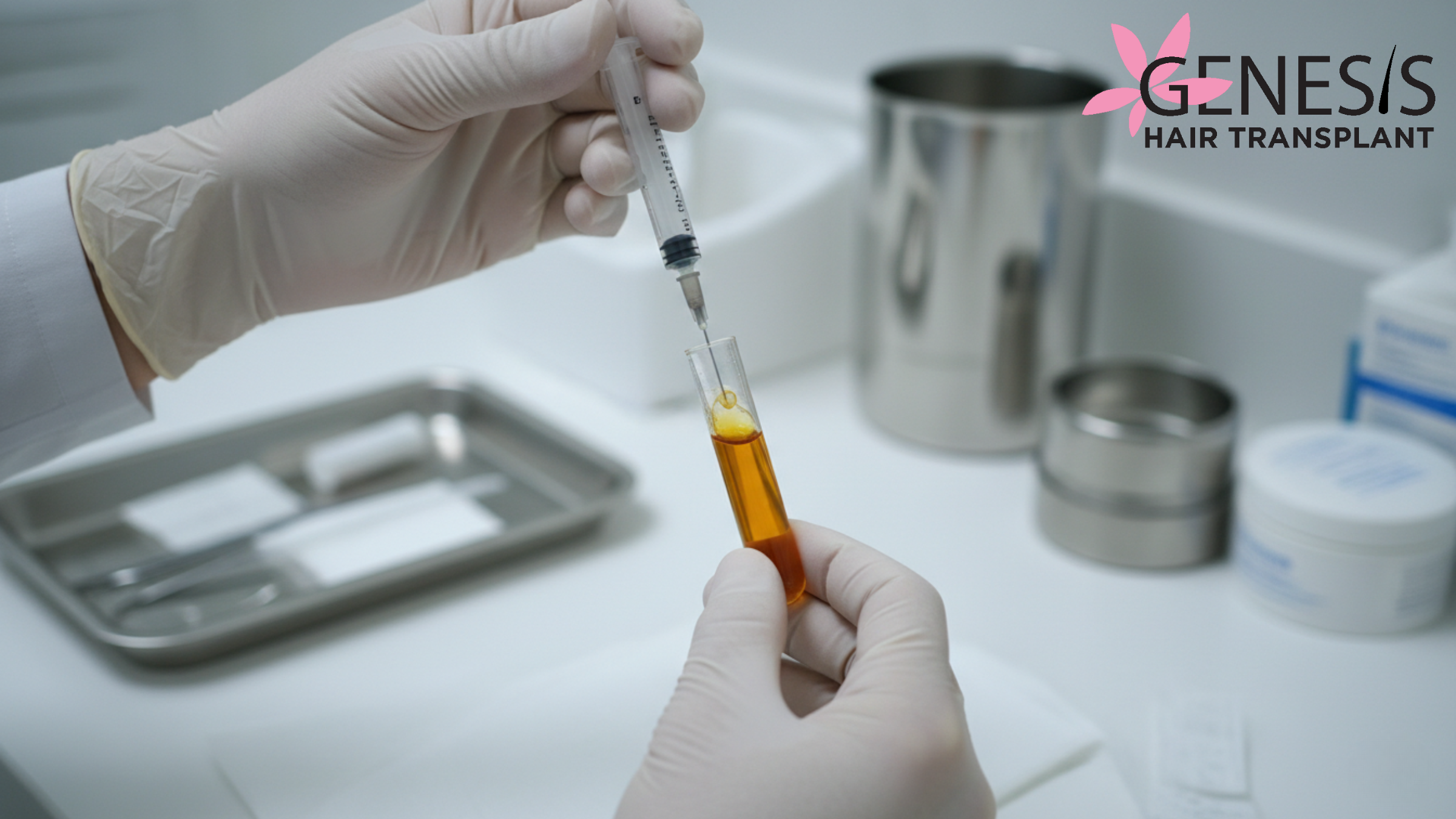
What Is PRP Treatment for Hair?
PRP Treatment for Hair stands for Platelet-Rich Plasma therapy. In this process, a small amount of blood is drawn from the patient and processed to extract platelet-rich plasma. These platelets are rich in growth factors. As a result, when injected into the scalp, they help strengthen hair follicles and improve blood circulation.
Therefore, PRP for hair Indore is commonly recommended for androgenetic alopecia, stress-related hair fall, and weak hair roots.
Key Benefits of PRP Hair Therapy
There are several advantages of PRP hair therapy Indore, especially when performed by experienced specialists.
-
Firstly, it reduces excessive hair fall
-
Secondly, it improves hair thickness and density
-
Additionally, it strengthens weak hair follicles
-
Moreover, it promotes natural hair regrowth
-
Finally, it is a non-surgical and safe procedure
Because of these benefits, PRP Treatment for Hair is often combined with medications or other treatments for better results.
PRP Treatment Procedure Step by Step
The procedure is simple and usually completed within 60 to 90 minutes.
-
First, blood is drawn from the patient
-
Then, it is processed in a centrifuge machine
-
After that, platelet-rich plasma is extracted
-
Finally, the PRP is injected into the scalp
Since the treatment uses your own blood, the risk of side effects is minimal. Therefore, many patients choose PRP Treatment for Hair as a safe option.
PRP Results: What to Expect?
PRP results in Indore vary from person to person. However, most patients notice reduced hair fall within the first month. Gradually, new hair growth may be seen after 3 to 4 sessions.
Furthermore, visible improvement in hair texture and volume usually appears after 3 to 6 months. For best outcomes, doctors often recommend multiple sessions.
PRP Treatment Cost in Indore
The PRP treatment cost in Indore depends on several factors. These include the clinic, doctor’s experience, number of sessions, and hair loss condition.
On average, the cost ranges between ₹3,000 to ₹7,000 per session. However, package deals may reduce the overall expense. Compared to surgical options, PRP Treatment for Hair is more affordable and requires no downtime.
Who Is an Ideal Candidate for PRP?
PRP is ideal for people with early hair thinning, mild to moderate hair fall, or weak hair roots. However, it may not be effective for completely bald areas. Therefore, consulting a specialist before starting PRP Treatment for Hair is essential.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PRP Treatment for Hair is a proven, natural, and effective solution for hair loss. With visible results, minimal risk, and reasonable pricing, it has become highly popular. If you are considering PRP for hair Indore, consult an experienced clinic to achieve the best possible results.
Our Blogs

19 Feb 2025 • 4 min read


